To understand why NFTs are bad for the environment, it is essential to understand first what they are and how they work. An NFT is a unique digital asset that is stored on a blockchain — essentially a decentralized ledger that records transactions securely and transparently.
Ethereum is the most extensively used blockchain for NFTs. However, Ethereum has long relied on proof of work (PoW) system, a consensus mechanism that is very dependent on enormous quantities of computational power to check and include transactions in the blockchain, which provides security and transparency but at an alarming environmental cost.
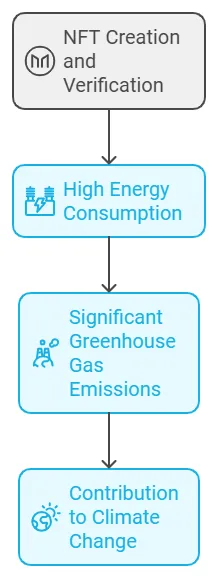
- NFTs contribute greatly to climate change due to the immense energy consumption required for their creation and verification on blockchain networks.
- The energy-intensive process of verifying NFT transactions on blockchain networks adds significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, making NFTs a major source of environmental concern.
What are NFTs?

NFTs are special digital items that prove ownership of unique online things like art or music. NFTs are like certificates for special digital stuff, kind of like owning a one-of-a-kind digital artwork.
They use a special computer system to make sure nobody can copy them. Ordinals are a new way to do this by putting the special information directly on Bitcoin. Both use a lot of energy to work.
The Birth of NFTs
Digital art used to be like a ghost online, easy to copy and share. But then NFTs came along in 2014 and changed everything. NFTs are special codes that say, “This art is mine!” It was like finding a treasure map for digital artists.
Now, people could buy and sell digital art just like real paintings. This opened up a whole new world for artists and collectors. It was like a big party for everyone interested in digital art.
Why are NFTs Bad for the Environment
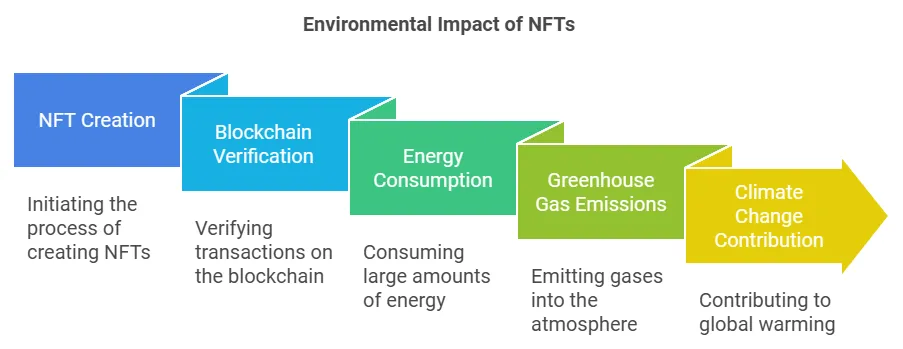
NFTs are bad for the environment because the process of creating and verifying them on the blockchain requires significant computing power, which often comes from energy sources that produce greenhouse gas emissions.
The high energy consumption of NFTs during creation, trading, and storage has become a major point of conflict due to their environmental impact. Here’s a closer look at how NFTs are bad for the environment.
Environmental Concerns: NFTs are linked to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
Energy Use: Making and keeping NFTs uses a lot of energy, which puts more pollution in the air.
Transaction Volume: The more people buy and sell NFTs, the more energy gets used, which puts more carbon dioxide in the air. This is why NFTs are bad.
Blockchain Energy Consumption: The biggest problem with NFTs is the amount of energy they use. This is because of the technology behind them, called blockchain.
Storage Impact: Storing NFTs on these networks uses a lot of energy, which makes more carbon dioxide in the air. This hurts the environment.
Popular Blockchains: Big names like Bitcoin and Ethereum are the most famous networks. Everyone uses Ethereum for digital art, such as pictures and stuff. But using Ethereum uses a lot of energy, which is why NFTs are bad for the environment.
Why are NFTs bad
NFTs have several drawbacks. They are often criticized for their high environmental impact, speculative nature, lack of fundamental value, potential for fraud, and contribution to digital waste.
Also, the digital shortage created by NFTs often drives speculative trading, contributing to market instability and potential financial losses for investors.
Energy Consumption in NFT Creation and Transactions
Making an NFT uses a LOT of energy. It’s like using 10,000 times more power than old ways to make things. This big energy use comes from computers solving hard puzzles to make the NFT work.
Every time you buy or sell an NFT, it uses even more energy. So, while NFTs can be cool, they’re not good for the environment.
This energy-intensive nature shows why are NFTs bad for the environment.
Making NFTs uses a lot of energy, at every step: creating them, putting them up for sale, buying and selling them, and even storing them.
- Making (Minting): The artist uploads their artwork to a special system that turns it into an NFT and keeps track of who owns it. This takes energy.
- Selling (Listing): Once made, the NFT goes on a marketplace like a store. This also uses some energy.
- Buying: When someone buys the NFT, the system checks everything is right and changes ownership. This takes more energy.
- Storing: The artwork itself isn’t stored on the special system, but somewhere else. Even this uses a little energy.
All this energy adds up, which is why some people are worried about the environment.
The Environmental Cost of Energy Consumption

Proof-of-Work (PoW) and its Energy Demands
Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles, with a winner winning the right to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. While good at security, though, this process has to consume energy.
To put it into perspective, PoW-based blockchains consume as much electricity as entire countries, contributing heavily to global energy demand.
NFT Transactions: A Power-Hungry Process
Every NFT minted or traded involves a chain of energy-intensive blockchain operations. Consider, for example, the tale of artist Joanie Lemercier, who learned that one NFT sale took approximately 8.7 megawatt-hours of energy—enough to power her studio for two years.
The energy cost of an NFT transaction isn’t theoretical but it has real-world implications. In terms of sheer consumption, the energy required to mint one NFT could power an average household for weeks. When critics ask why are NFTs bad? This unsustainable energy demand is one of the major reasons.
Carbon Emissions from Non-Renewable Energy
The majority of the power networks powering the blockchain network are powered by fossil fuels. As the NFT market increases, so does their carbon footprint.
Coal and natural gas reliance has made blockchain an enormous contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. This brings us back to a critical question: why are NFTs bad for the environment? It is the emissions-heavy infrastructure supporting them.
The overlooked aspect of NFTs’ environmental impact is electronic waste. Cryptocurrency mining relies on high-performance hardware, such as GPUs, which operate at full capacity, leading to a growing pile of discarded equipment.
This e-waste contains hazardous materials like lead and mercury. When improperly disposed of, these substances can leach into the environment, contaminating soil and water sources.
E-Waste Disposal and Its Environmental Impact
The poor disposal of mining equipment has further contributed to e-waste. Even though some of these rigs are recycled, many of them actually end up in the landfill where risks to environmental dangers from the toxic parts persist.
Even when recycling is attempted, the process can be resource-intensive, requiring high inputs of energy. These challenges show another reason why NFTs are bad for the environment—their indirect contribution to the global e-waste crisis.
Recycling Limitations
Although theoretically recycling should cut some of these problems, in the real world, things are more complex. Even though most regions do not have a proper structure for the recycling of e-wastes, in many areas where the infrastructure is available not all the material can be recovered. Besides, the energy needed to recycle outweighs the benefits to the environment, leading to an overall negative effect.
NFTs create almost negligible environmental challenges. Innovators are working towards reducing the ecological footprint of blockchain technology. So, can we turn the tide on why NFTs are bad for the environment? Let’s take a glance at the key mitigation efforts that are gaining traction.
Transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Why does this matter? PoS eliminates such energy-intensive mining operations, which by their sheer nature would cut down the overall energy consumption as much as 99.95%. It makes PoS a game-changer in reducing the carbon footprint of NFT transactions, so it can address one of the primary reasons why NFTs are bad.
The most promising solution lies in Ethereum’s shift from a proof-of-work (PoW) system to proof-of-stake (PoS). This upgrade fundamentally alters how transactions are validated.
Renewable Energy Adoption
Another significant measure of the reduction of the NFT-causing negative impact on the environment could be the use of renewable power sources in the functioning of blockchain. Some visionary mining plants have actually taken the initiative to integrate solar, wind, and hydroelectric power sources into their functioning.
Projects like Tezos and Algorand, and many others, are designed with considerations to energy efficiency; they often claim their commitment to sustainability. The use of clean energy actually reduces the demand for fossil fuels, hence cutting the carbon footprint issue at its root.
The Bottom Line
NFTs use a lot of energy. They are bad for the environment because they consume a lot of energy.
Creating, selling, buying, and even storing NFTs requires significant energy, which often comes from fossil fuels. This contributes to climate change. Essentially, the process of turning art into an NFT and handling its transactions is very energy-intensive.
FAQ's
Why is crypto so bad for the environment?
Crypto mining consumes huge amounts of energy, contributing to carbon emissions and climate change.
What are the negatives of NFT?
NFTs often rely on energy-intensive blockchain technology, leading to environmental concerns and unstable market conditions.
What is the biggest problem with NFTs?
The energy-intensive mining process is the biggest problem associated with NFTs.