Renewable resources refer to those natural resources, which over time can replace themselves. Some common renewable resources include solar, wind and water, which can be used to generate electricity, produce heat, and fuel transportation.
By using renewable resources, we can reduce our reliance on finite resources, reduce the impacts of climate change, and ensure a healthier planet.
The path of sustainability to a future depends highly on our ability to work in pair with the powerful nature itself. Renewable energy from sunlight, wind, and flowing water is all abundantly available and continuously restored, promising not just a cleaner but an entirely sustainable future. By doing this, we can eventually rely less on finite sources of energy like fossil fuel, reduce environmental damage, and create ways toward a more balanced relationship with our planet.
Renewable energy sources nowadays already account for a significant percentage of electricity generation worldwide, revealing rapid growth and increasing value in the transition to the future of a more sustainable energy.
But what are renewable resources, and why are they so vital? Let’s dive in.
What are Renewable Resources

Renewable Resources Definition
Renewable resources are natural materials that can be restored at a rate that effectively replaces what is consumed, ensuring a continuous supply over time.

What is a Renewable Resource
Renewable resources are natural resources that can regenerate themselves through natural processes within a relatively short period.
Unlike finite fossil fuels, these resources do not exhaust themselves if used sustainably. They are like hitting the reset button in nature. From sunlight to wind, these natural renewable resources are the ultimate power players in the fight for sustainability.
Mind-Blowing Facts
- A portion of the Sahara Desert could potentially power the entire world with solar energy.
- Global wind power capacity now surpasses the total coal-fired power generation in China.
- The ocean’s movements contain immense energy, enough to power entire cities.
Characteristics of Renewable Resources
What makes a resource “renewable”? Here are the key features that define them:
- Regeneration Rate: They regenerate faster than we consume them.
- Sustainability: They have minimal environmental impact when used responsibly.
- Abundance: Many natural renewable resources, such as sunlight and wind, are practically limitless.
For example, the energy we obtain from the sun—solar power—is a daily miracle that powers homes, businesses, and even vehicles.
Types of Renewable Resources

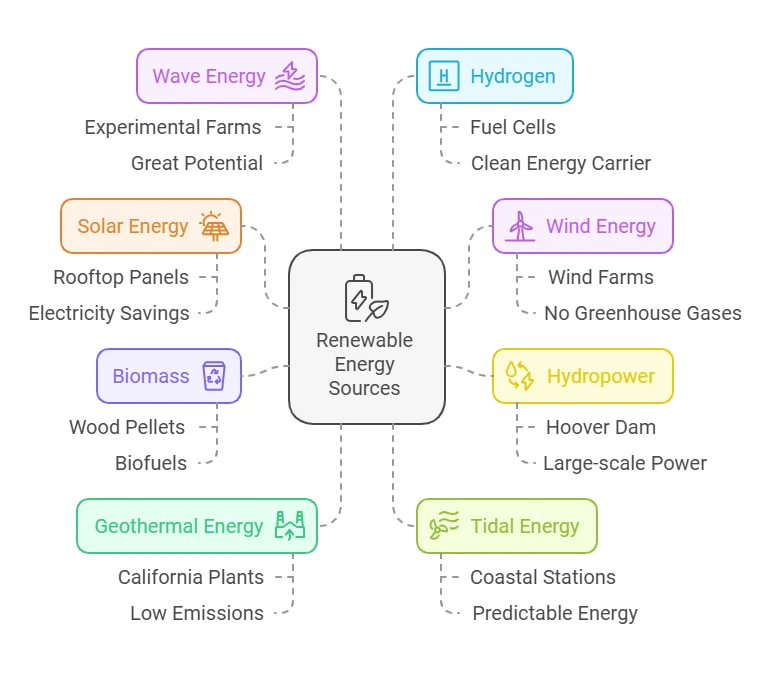
1. Solar Energy
Solar energy captures the sun’s rays through solar panels and converts them into electricity. It’s abundant, cost-effective in the long run, and has a least carbon footprint.
- Example: Rooftop solar panels powering homes across the U.S.
- Key Benefit: Reduces reliance on fossil fuels while lowering electricity bills.
2. Wind Energy
Utilizing wind through turbines is one of the fastest-growing energy sources worldwide.
- Example: Wind farms in the Midwest generating clean power.
- Key Benefit: It’s renewable, scalable, and produces no greenhouse gases during operation.
3. Hydropower
Hydropower uses flowing water to generate electricity, often through dams.
- Example: The Hoover Dam provides power to millions.
- Key Benefit: Reliable and capable of large-scale energy production.
4. Biomass
Biomass consists of organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, and even algae, which can be converted into energy.
- Example: Using wood pellets for heating or biofuels for transportation.
- Key Benefit: Multifunctional and reduces waste by repurposing organic materials.
5. Geothermal Energy
This utilizes the Earth’s internal heat to generate electricity or provide direct heating.
- Example: Geothermal plants in California supplying consistent energy.
- Key Benefit: Steady energy output with least emissions.
6. Tidal Energy
Tidal energy captures the power of ocean tides to generate electricity.
- Example: Coastal tidal power stations.
- Key Benefit: Predictable and highly efficient in suitable locations.
7. Wave Energy
Wave energy utilizes the motion of ocean waves to produce power.
- Example: Experimental wave farms in the Pacific Northwest.
- Key Benefit: A promising, unused resource with great potential.
8. Hydrogen
Hydrogen, produced using renewable electricity, serves as a clean energy carrier for fuel cells.
- Example: Hydrogen-powered vehicles.
- Key Benefit: Zero emissions and high energy efficiency.
Examples of Renewable Resources

These are renewable resources examples:
1. Sunlight
Utilized through solar panels for residential electricity.
2. Wind
Captured by wind turbines in wind farms, such as those in Texas.
3. Water
Used for hydropower, like the Hoover Dam generating electricity.
4. Wood and Crops
Burned or converted into biofuels, such as ethanol from sugarcane.
5. Geothermal Hot Springs
Tapped for geothermal energy production, especially in places like Iceland.
6. Ocean Waves
Utilized by experimental wave energy converters.
7. Hydrogen
Obtained from water electrolysis and used in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
The Importance of Renewable Resources
Environmental Benefits
- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Unlike fossil fuels, renewable resources release little to no harmful gases.
- Biodiversity Conservation: By reducing pollution, conservation of renewable resources helps protect ecosystems and wildlife.
Economic Advantages
- Job Creation: The renewable energy sector generates jobs in installation, maintenance, and innovation.
- Cost Savings: While initial investments can be high, long-term savings are significant.
Energy Security
- Diverse Energy Mix: Reducing dependence on imported fuels strengthens national security.
- Stable Prices: Renewable resources prices are less unstable compared to fossil fuels.
Challenges Facing Renewable Resources
Variability Issues
Some renewable resources, such as solar and wind, depend on weather conditions.
Solution: Advanced energy storage systems, such as batteries, can store excess energy for later use.
Initial Costs
Renewable infrastructure, such as wind turbines and solar panels, requires a significant upfront investment.
Solution: Financial incentives, government subsidies, sustainable technology and technological advancements are making renewables more accessible.
Land Use Concerns
Large-scale projects can compete with natural habitats or agricultural land.
Solution: Strategic planning to balance development and conservation of renewable resources.
Future Trends in Renewable Resources
Technological Innovations
From improved solar panel efficiency to floating wind turbines, technology is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Policy Developments
Governments worldwide are introducing policies to promote renewable energy adoption, including tax credits and renewable energy mandates.
Public Awareness and Community Engagement
Educational initiatives are empowering individuals to adopt sustainable practices, from installing solar panels to supporting conservation of renewable resources policies.
The Bottom Line
What are renewable resources? They’re not just the future—they’re the present. By embracing solar, wind, hydropower, and other natural renewable resources, we can combat climate change, boost economies, and secure a brighter future.
So, why not start today? Support renewable initiatives, explore sustainable resources examples, and join the global movement toward a greener planet.
Further Resources
- International Renewable Energy Agency: Comprehensive insights into renewable energy.
- U.S. Department of Energy: Explore renewable energy initiatives and projects.
- Suggested Reading: “Renewable Energy: Power for a Sustainable Future” by Godfrey Boyle.
FAQ's
What are 5 examples of renewable resources?
Solar, wind, water, geothermal, biomass
What are renewable sources?
Resources that naturally restore themselves, such as sunlight and wind.
What are the 3 main renewable resources?
Solar, wind, and hydropower.
What is renewable and nonrenewable?
Renewable resources can be naturally replenished (e.g., sunlight), while non-renewable resources are finite and will eventually run out (e.g., fossil fuels).




