Sustainability balances present needs with the preservation of resources for the future.
We have to make smart uses of our resources not in such a way that hurts the environment. Simple things such as waste reduction and saving energy can create a healthful planet for all of us.
What if the way we live today could guarantee a better tomorrow? That’s the nature of sustainability — a philosophy and practice aimed at meeting our needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs. In a world struggling with climate change, resource depletion, and social inequality, sustainability is no longer optional. It’s essential.
This guide will teach you about sustainability, give you practical tips, and inspire you to make a difference.
What is Sustainability

Sustainability is the practice of meeting our present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
It refers to balancing environmental, social, and economic considerations for long-term health and well-being. This means being aware of the importance of biodiversity and using resources efficiently, reducing waste, and protecting the environment.
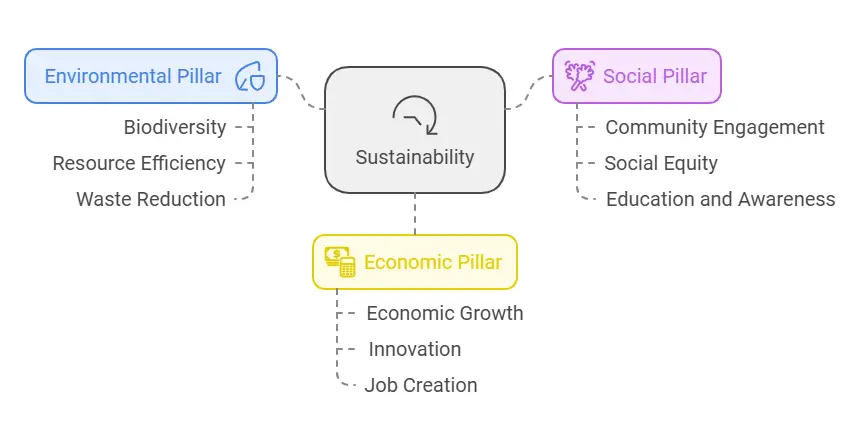
In such an effort, the backbone remains formed by three pillars — that are, environmental, social, and economic. Together, they focus on the connection of our planet’s ecosystems, communities, and economies. Let’s find why it is more important now to adopt sustainable practices.
Sustainability Definition
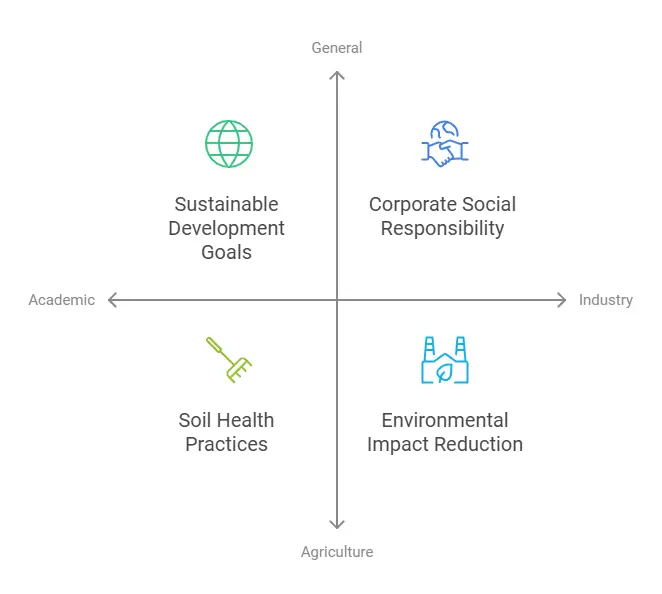
Academically, sustainability is often defined through the lens of sustainable development, which is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
In industry, definitions can vary. For example, in business, sustainability might focus on corporate social responsibility (CSR), which includes ethical practices, reducing environmental impact, and improving social welfare.
In agriculture, sustainability refers to practices that maintain soil health, conserve water, and reduce chemical use to ensure long-term productivity.
Sustainability Explanation

Context History
Sustainability as a term did not come overnight. Its basis is traced back to the ancient civilizations that practiced resource conservation. However, the term became famous with the 1987 Brundtland Report that introduced the concept of “sustainable development.” Global summits, such as the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio, further placed it on the world’s agenda, making environmental sustainability a priority.
Core Principles of Sustainability
- Interdependence: All life forms are interconnected, and our actions have consequences in ecosystems all over the world.
- Equity: Equitable access to resources and opportunities for all; closing the gap between the privileged and the underserved.
- Long-term Thinking: Thinking about future generations, not just short-term gains.
These three principles guide policy, practice, and sustainable lifestyle choices that lead to sustainable development and overcome the challenges of modern times.
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals established by the United Nations in 2015. They are designed to address a wide range of issues, from poverty and hunger to climate change and inequality, by 2030.
The SDGs provide a complete blueprint for achieving a more sustainable and equitable world. They are a call to action for all countries to work together to tackle global challenges and assuring a better future for all.
The Three Pillars of Sustainability

Environmental Sustainability
Think of environmental sustainability as the insurance policy of the planet. It is the preservation of natural resources and ensuring that the ecosystems are healthy. Here is how it can be done:
Renewable Energy: Shifting to solar, wind, and other clean energy sources reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting forests, oceans, and wildlife preserves biodiversity.
Waste Management: Recycling and composting minimize landfill waste and reduce pollution.
For instance, adopting green living practices such as the use of energy-efficient appliances cuts down your carbon footprint while saving money.
Social Sustainability
At the core of social sustainability lies the preservation of equitable and vibrant communities. These are inclusive, educational, and ensure a quality life.
Inclusivity: Diversity is supported with equal opportunities for all.
Education: Knowledge enabled to take part in sustainable practices.
Quality of Life: Building safe and healthy environments with access to healthcare, housing, and clean water.
Social sustainability connects the divide between privilege and poverty, as making eco-friendly living accessible to all is social sustainability.
Economic Sustainability
The backbone of economic sustainability is an economy that functions well without exploiting resources or people. It’s all about:
- Responsible consumption, which involves minimal waste and mindful purchasing.
- Ethical business practices, such as ensuring fair wages and sustainable supply chains.
- Circular economy models, designing products that can be reused, repaired, or recycled.
Imagine businesses that make money but also care about the environment and society. That is what it is meant to be.
Current Challenges to Sustainability
Climate change displays itself through increased temperatures and extreme weather events. It has several impacts:
- Melted ice caps and rising sea levels
- Ecosystem disruption and extinction of species
- Food and water insecurity
Shifting to renewable energy sources and sustainable agriculture methods are key mitigation measures.
Resource Depletion
Our planet’s resources are finite, yet overconsumption continues. Consider these facts:
| Resource | Current Challenges | Sustainable Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Water | Overuse and contamination | Conservation and desalination |
| Forests | Deforestation for agriculture and logging | Reforestation and agroforestry |
| Minerals | Unsustainable mining practices | Recycling and responsible sourcing |
Social Inequality
Sustainability is not only for the environment. Social issues such as income inequality, resource distribution, and poor resource access are also problems for global progress. Here lies the foundation in making social sustainability last longer.
Strategies for Sustainability Building
Personal Actions
Many little changes can make the difference. Here are everyday practical tips on embracing green living.
- Compost and use fewer wasteful products to conserve resources.
- Use LED light bulbs and smart thermostats to save electricity.
- Supporting eco-friendly brands that put sustainability first.
Sustainability in Everyday Life
Achieving sustainability starts with individual actions. Here are some practical tips:
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Reduce waste by reusing items and recycling materials whenever possible.
- Responsible E-Waste management: Learn about e-waste before discarding the electronic devices, especially old cell phones or computers in a landfill.
- Conserve Energy: Use energy-efficient appliances, turn off lights when not in use, and consider renewable energy sources such as solar panels.
- Save Water: Fix leaks, use water-saving fixtures, and be mindful of water usage in daily activities.
- Support Sustainable Brands: Purchase from companies that prioritize sustainable practices and fair trade.
- Eat Sustainably: Choose locally-sourced, organic foods, and reduce meat consumption to lower your carbon footprint.
- Shop Sustainably: Choose sustainable products while shopping.
- Recyclables: Learn about recyclable items.
- Individual action: Picking up trash directly adds to environmental cleanliness, fights littering, and promotes a sense of community responsibility.
Community Actions
Communities are important agents of change. Here are some good examples:
Urban Gardens: Using abandoned lots as food production sites.
Clean-Up Drives: Reducing local pollution and boosting community pride.
Local Policies: Performing waste separation and recycling schemes.
When communities unite, sustainable development becomes a story of mutual success.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Companies make a difference in sustainability. The top brands are adopting practices such as:
CSR Initiatives: Funding environmental and social programs.
Sustainable Supply Chains: Ethical sourcing and minimal waste.
Transparency: Publishing sustainability reports to build trust.
Holding businesses accountable ensures progress on a larger scale.
Sustainable Technology

Technological Advances
Tech is changing the way we approach sustainability. Some of the key innovations include:
Renewable Energy Technologies: Advancements in solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage.
Electric Vehicles: Reducing emissions with EVs and expanded charging infrastructure.
Smart Grids: Efficient use of energy distribution to reduce wastage.
Sustainability Through Technology
- Edge computing supports sustainability by bringing computing power closer to the action, saving energy and helping us react faster to things around us.
- Role of blockchain in sustainability is like a super safe list of everything that keeps things honest and fair, cutting down on waste.
- Using energy wisely is key. By using less and choosing smart energy like solar and wind, we can clean up our air and even power cool tech such as NFTs without hurting the Earth.
Feeding the world in a sustainable way is possible through methods like:
Permaculture: Designing farms such as natural ecosystems.
Organic Farming: Avoiding pesticides that are harmful to health and soil health.
Agroforestry: Combining trees and crops to boost productivity.
These practices ensure food security while protecting the planet.
Circular Economy Models
The traditional “take, make, dispose” model is being replaced by the circular economy, which focuses on:
- Recycling materials to reduce waste.
- Designing products for durability and reparability.
- Encouraging sharing economies (e.g., car-sharing, tool libraries).
This shift reduces pressure on resources and promotes sustainable economic growth.
The Role of Policy in Sustainability
Government Initiatives
Governments worldwide are stepping up with policies to tackle climate change and promote sustainability. Examples include:
- Paris Agreement to reduce global warming
- Tax breaks on renewable energy-based projects
- Single-use plastics banned
Regulatory Frameworks
Effective regulations guarantee that the industrial sectors will stick to green practices. These are;
- Emissions standards for automobiles and factories
- Policies on sustainable agriculture that help prevent land degradation
- Legislation on waste management and recycling
Governments, businesses, and citizens should work together to achieve this.
The Bottom Line
Sustainability is the blueprint for a brighter, greener future. We can tackle some of the world’s most urgent problems and build the way for generations to thrive if we embrace environmental, social, and economic sustainability.
So, what can you do today to make a difference?
Start small: switch to eco-friendly products, join a local initiative, or advocate for sustainable policies. Together, our efforts can create ripples of change.
Check out resources such as the World Wildlife Fund and the Sustainable Development Solutions Network to better understand what you can contribute to the sustainable world we live in.
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF): https://www.worldwildlife.org
- Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN): https://www.unsdsn.org
FAQ's
What does sustainability mean?
Sustainability means meeting our needs without hurting the planet or future generations.
What are the 3 main principles of sustainability?
- Environmental: Protecting nature.
- Social: Fair for everyone.
- Economic: Good for the economy.
What is sustainability in one word?
Viability
What are the 4 types of sustainability?
- Environmental
- Social
- Economic
- Cultural




