The needs for processing data are increasing enormously in this connected age. Cloud computing, though impressive, involves data transfer over quite long distances, resulting in huge energy consumption and devastating the environment.
Edge computing promises a solution. Closer to the source, in a more localized approach towards data processing, edge computing drives us into a sustainable future for all industries, across all sectors.
Edge Computing and Sustainability

Edge computing improves sustainability through saving energy, optimizing resource utilization, and enabling real-time environmental monitoring through local data processing. Edge computing simply allows data to be processed and checked near its source, which can greatly upgrade the performance and results of various applications.
It is especially beneficial for sustainable technology and sustainability efforts, reducing the need for long distance data transfer, which in turn lowers energy use and improves response times.
For instance, in an industrial setup, edge computing can help machines check data locally to detect problems and enhance performance in real time.
Do You Know
According to a report by Gartner, by 2025, 75% of enterprise generated data will be processed at the edge, up from less than 10% in 2018. This shows how edge computing is becoming more important in today’s technology world.
Markets and Markets have estimated that the global edge computing market will rise from $4 billion in 2020 to $15.7 billion by 2025.
Understanding Edge Computing
Imagine instead of sending all your data to a distant server that you could process it right where it’s generated, on your local device, a nearby server, or within the same building. That is a very fundamental definition of the essence of edge computing. Its essence lies in the ability to utilize computing resources near the data source, giving faster processing, reduced latency, and improved data security.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing processes data closer to its source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. It involves implementing computing resources at the network edge, such as in local data centers or devices. This approach enables faster response times, improved data privacy, and lower operational costs.
Edge computing is essential for applications requiring low latency, high bandwidth, and real-time processing, such as autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and industrial IoT.
How can Edge Computing be used to Improve Sustainability

Edge computing enhances sustainability through energy consumption reduction, resource optimization, and real-time environmental monitoring. It enhances efficiency in smart cities, healthcare, and manufacturing, thus contributing to a greener future.
Edge computing is crucial for sustainability. It reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with data transfer by processing data closer to its source. This local approach also accelerates operations, allowing for real-time decision-making and resource enhancement.
From cutting energy waste in smart grids by as much as 20% to reducing traffic congestion and emissions in cities by 30%, edge computing brings big environmental benefits.
Its applications span several sectors: healthcare, manufacturing, agriculture, and waste management, making it an essential tool for a greener future.
Sustainability Benefits of Edge Computing
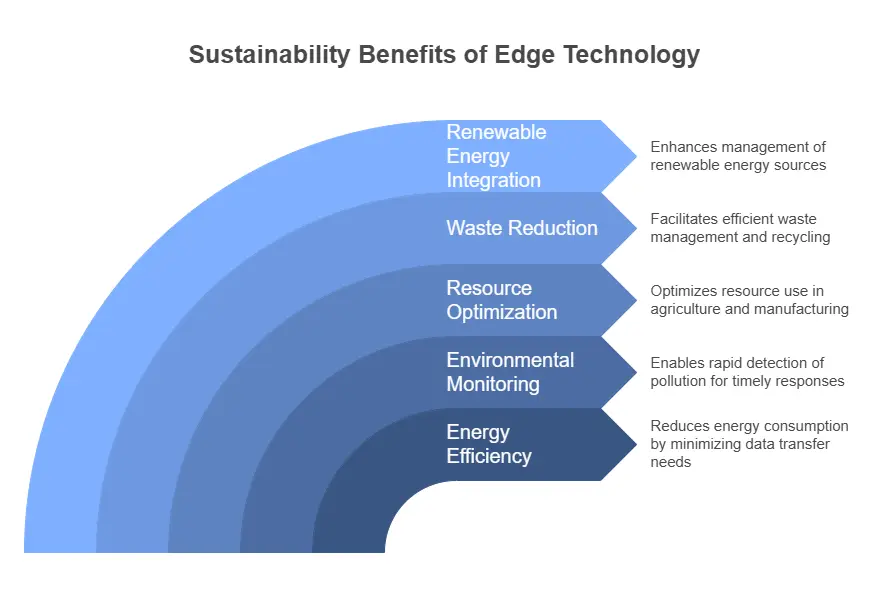
Edge computing increases sustainability through reduced energy consumption, optimized resource use, and real-time environmental monitoring.
Energy Efficiency
- Edge computing significantly reduces energy consumption that comes with data transfer by minimizing the need to transfer data over long distances.
- Devices for edge computing are generally smaller and less energy-intensive than large data centers, hence further contributing to energy savings.
Environmental Monitoring
- Real-time data processing at the edge gives power to environmental monitoring initiatives. Field-deployed sensors can rapidly detect air pollution and water pollution, thus quickly responding to environmental challenges.
- This is especially useful in areas with little or no connectivity, thereby providing timely conservation efforts and disaster response.
Resource Optimization
- In sustainable agriculture, edge computing assists in precision farming by scrutinizing real-time data with respect to soil conditions and weather patterns along with crops’ health. It helps optimize water usage, minimize applications of fertilizers, and reduce environmental footprint.
- It helps manufacturing organizations in providing real-time process monitoring with predictive maintenance to reduce their equipment downtime and minimize wastage.
Waste reduction
- Edge computing plays an important role in waste management: it facilitates real-time observation of the level and make-up of waste bins for optimized collection routes, decreases landfill waste, and encourages the recycling industry.
Renewable Energy Integration
- Edge computing improves renewable energy sources in the forms of solar or wind. Data processing directly at the edge allows the real-time management of grid systems with optimal energy transmission and zero energy waste.
Real-Life Applications of Edge Computing
Smart Cities: edge computing enables smart city initiatives for real-time traffic management and optimization of public transportation services, and more efficient city planning.
Healthcare: edge computing in healthcare allows patients to be remotely monitored which leads to quicker diagnosis and the treatment process.
Industrial IoT: edge computing is turning industrial operations upside down to enable predictive maintenance, thus improving production efficiency and reduction of environmental impacts.
Case Study: Smart Grid in Europe
A smart grid project in Europe used edge computing to improve the accuracy and outcome of power distribution. Edge devices installed throughout the grid monitored energy flow and adjusted distribution in real-time.
This method reduced energy wastage and improved the combination of renewable energy sources, leading to a more sustainable power system.
Case Study: Smart City in Asia
In an Asian metropolis, edge computing powered a range of smart city features especially to sustainable transport system. Traffic management systems used edge devices to reduce blockage and emissions, while smart utilities improved water and electricity usage.
These efforts improved urban living conditions and added to big energy savings and environmental benefits.
Case Study: Healthcare in North America
A North American healthcare provider started edge computing to improve patient monitoring and reduce energy use. Wearable devices monitored patients’ vital signs and processed data locally, allowing for instant medical response.
This system improved patient outcomes while reducing the energy needed for data transfer and storage.
Conclusion
Edge computing is good for the environment as it uses relatively less energy. This it does by keeping data next to where it was manufactured, so it does not travel far.
So, how can edge computing be used to improve sustainability? — It supports sustainability in various fields of technology and life.
Edge computing is not only technology but also a foundation for a greener future. It allows data processing close to the source and provides us with the opportunity to use resources efficiently, minimize damage to the environment, and build a more resilient, sustainable world with better sustainable solutions.
Further applications of edge computing will become even more innovative, which will be critical to resolving environmental issues and making our tomorrow greener.
FAQ's
How can computing be used to improve sustainability?
Edge computing improves sustainability by reducing energy consumption, improving resource use, and enabling real-time decision making for a sustainable future.
What are the 5 benefits of edge computing?
- Faster Speeds: Data is processed locally, leading to quicker responses.
- Improved Reliability: Systems can continue working even if the main internet connection fails.
- Enhanced Security: Data stays closer to its source, reducing the risk of it being stolen.
- Reduced Costs: Less data needs to travel long distances, saving money.
- Greater Efficiency: Real-time decisions can be made, improving how things operate.
How does edge computing help?
Edge computing brings data processing closer to where it happens. This makes things faster, safer, and more efficient. It’s like having small computers work nearby instead of sending everything far away.




