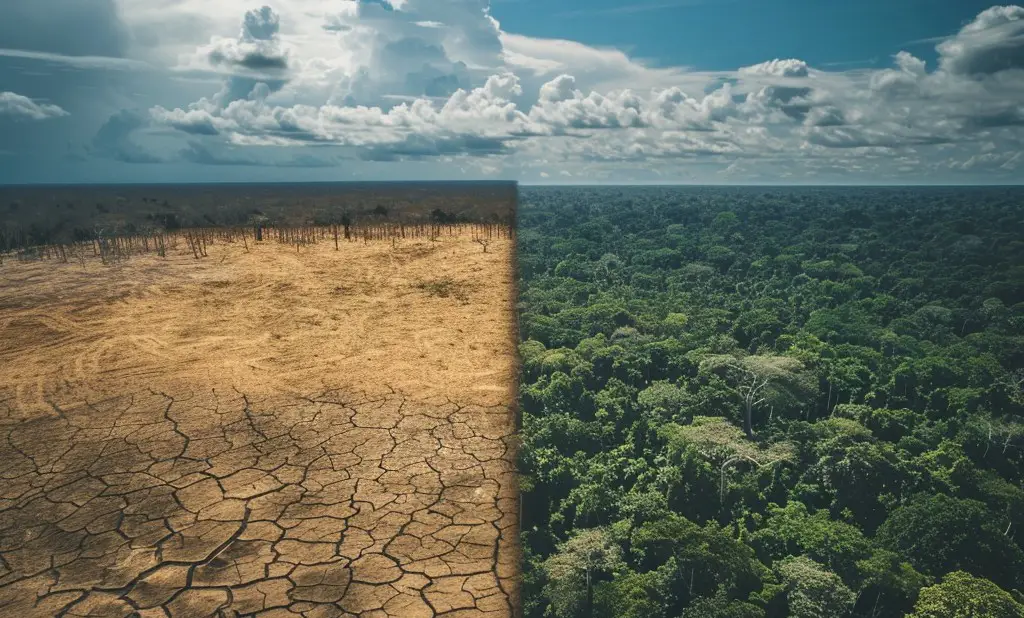
Deforestation. It is a term we hear constantly, but we underestimate its magnitude. A phenomenon that was once strictly local has grown into an international crisis-the large-scale destruction of forests for agriculture, urbanization, and industrialization.

Why should we be concerned?
Deforestation affects more than just trees; it destroys ecosystems, accelerates climate change, and disrupts the balance of life. The urgent need to understand and counter the impact of deforestation cannot be overstated.
Forestry covers around 31% of Earth’s surface. They’re being lost at alarming rates. In recent research studies, around 10 million hectares are being lost annually. Here are some far-reaching implications that this blog focuses on related to biodiversity, climate, soil, and water resources, among other topics, which result from the effects of deforestation.

Destruction of Habitat
Deforestation means denying numerous species of their habitats. Forests make up about 80% of the terrestrial biodiversity, providing essential homes for animals, plants, and microorganisms. Upon losing forests, the complexity of these ecosystems is completely disrupted.
Consider the example of hotspots such as tropical rainforests. They harbor iconic species such as jaguars, orangutans, and toucans. However, excessive deforestation makes these creatures homeless, thus driving a good number to the brink of extinction.
Species Extinction
The negative effects of deforestation extend beyond habitat loss. Without adequate shelter and resources, countless species face extinction. For instance, the Sumatran tiger and orangutan populations have decreased significantly due to deforestation-driven habitat destruction. Experts estimate that deforestation contributes to the extinction of 137 species every single day.
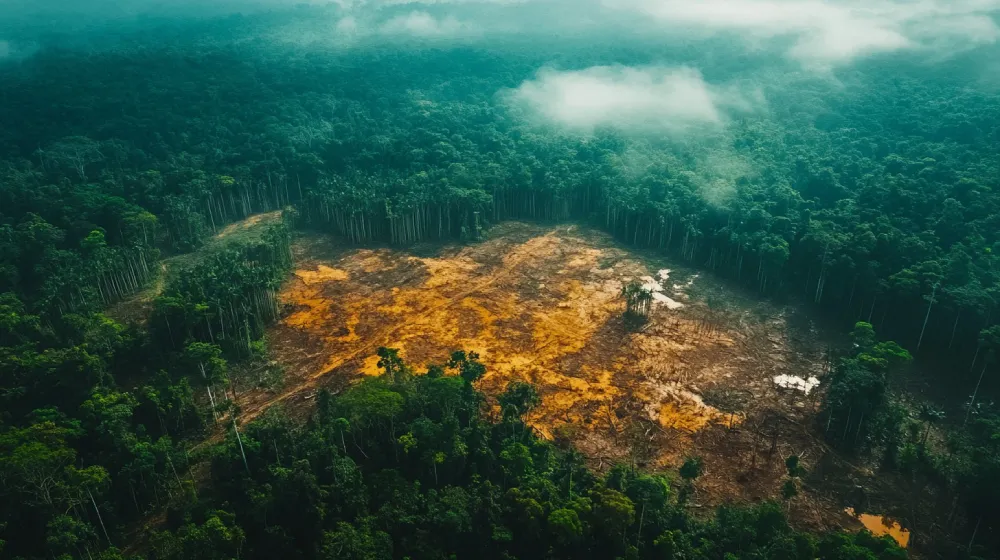

Increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Trees are usually known as the “lungs of the Earth” because of how trees absorb carbon dioxide and leave out oxygen in return, therefore maintaining the earth’s atmosphere. Carbon is emitted to the atmosphere by falling trees that burn during deforestation. About 10 percent of the world’s emissions from greenhouse gases originate from deforestation that causes air pollution and global warming.
Global Warming
The climate impact of deforestation goes beyond carbon emission. The Earth’s surface heats up more without forests, leading to increased temperatures. This is what leads to a break in weather conditions, extreme heat waves, and upsets the ecosystems as a whole. Global warming is linked to the impact of deforestation in undeniable terms and with pressing urgency.
Disruption of the Water Cycle
Altered Precipitation Patterns
Forests play a vital role in maintaining the water cycle. Water vapor is released into the atmosphere by trees through a process called transpiration, which leads to rainfall. The removal of forests breaks this cycle, resulting in reduced rainfall and increased drought frequency.
Loss of Soil Moisture
Deforestation effects extend underground. Without tree roots, soils dry out faster. This affects agriculture because crops cannot grow well in dry conditions, and it disrupts natural vegetation.
Soil Erosion and Degradation
Increased Soil Erosion
Trees have roots that stabilize the soil from erosion. Once the forest is cleared, that stability is lost and will lead to increased soil erosion. Rivers and streams, which are clogged with eroded soil, alter water quality and greatly disrupt aquatic systems.
Nutrient-Rich Topsoil Loss
Forests represent a natural reservoir of nutrient-rich topsoil essential for agriculture. Removing the same depletes the important resource and leaves lands with barren lands and lower productivity in agriculture. It seriously threatens food security in several regions.
Increased Flooding and Natural Disasters
Flood Risks
Forests serve like natural sponges through absorbing the excess rainfall and therefore resulting in fewer chances of a flood. Without the absorptive layer, water resulting from rain flows freely leading to devastating floods. Southeast Asian regions have experienced increased flooding associated with extensive deforestation.
Natural Disaster Frequency
Deforestation brings about more frequent floods besides making areas prone to storms and landslides. Deforestation creates an instability in the soil and weather which leads to the frequent and sometimes severe natural calamities.
Impact on Indigenous Communities
Displacement and Livelihood Loss
To the many Indigenous communities, the forests do not only provide but represent a way of life, with forests serving as means for food, medicine, and cultural practice. Such communities are uprooted and deprived of their habitat and livelihood through deforestation.
Cultural Effects
The loss of forests therefore corresponds to the loss of heritage: the traditional knowledge and cultural practices associated with the ecosystems are diminished, and there is disconnection with one’s ancestral roots.
Economic Consequences
Impact on Ecosystem Services
Forests provide essential ecosystem services, such as clean air, water filtration, and climate regulation. The negative impacts of deforestation on these services have broad economic implications. For example, the loss of pollinators due to habitat destruction can cost billions in agricultural losses annually.
Costs of Deforestation
While it may bring some immediate economic benefits, long-term costs tend to be greater than short-term gains from deforestation. Restoration projects, loss of biodiversity revenue, and climate change mitigation efforts place heavy financial burdens on governments and communities
Conclusion
Deforestation is a crisis of diverse dimensions with critical implications for biodiversity, climate, water cycles, and soil health and human livelihoods. It has widespread impacts, posing threats to the environment and the socio-economic and cultural fabric of societies globally.
Now is the moment to act in order to mitigate the effects. Conserve, promote sustainable practices, and advocate for policy changes that will truly help preserve Earth’s forests for future generations. Together, we can change the course of history on deforestation and a better green planet.
FAQ's
What are the effects of deforestation?
Deforestation leads to climate change, loss of biodiversity, soil erosion, and water cycle disruption.
What are 3 results of deforestation?
Three 3 major results of deforestation are greenhouse gas emissions, habitat loss for countless species, and increased soil erosion.
What is the problem with deforestation?
Deforestation harms the environment and contributes to global warming.
Why should we stop deforestation?
We should stop deforestation to protect the environment, combat climate change, and preserve biodiversity.




